Rubber Transfer Molding Process
Shalimar uses the rubber transfer molding process to produce a full range of precision molded rubber and rubber-to-metal bonded components. The benefits of transfer molding are seen in mid to high volume production, tight tolerance, over-molding and applications with colored or translucent materials. The transfer molding process combines attributes of both injection and compression molding making it an ideal manufacturing method for many applications.

Rubber Transfer Molding Process Description:
Transfer molding, unlike compression molding uses a closed mold system. The process begins with a piece of uncured rubber that has been preformed to a controlled weight and shape. The preform is placed into the portion of the mold called a "pot" located between the top plate of the mold and the ram (image right). The ram is closed which distributes (transfers) the uncured rubber into the cavity(s) through a runner and gate system. The material is held under high pressure and temperature to activate the cure system in the rubber compound (rubber is vulcanized). The cycle time is established to reach an optimal level of cure. At the end of the cycle, the parts are removed or ejected from the cavitiesand the next cycle begins.Advantages of Rubber Transfer Molding:
- Shorter production cycle times compared to traditional compression molding
- Supports high precision molding applications
- Advantages for colored or translucent compounds
Disadvantages of Transfer Molding vs. other rubber molding methods
- Pot system can increase gross material weights when cold pot or other low waste options are not utilized
- Higher tooling cost compared to traditional compression tools
For more information on the rubber and plastic design processes please visit our rubber design section.
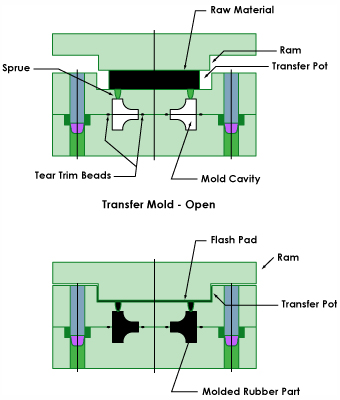
Rubber Transfer Molding Steps:
- Uncured rubber is preformed to control weight, shape and specification
- Rubber preform is placed into pot
- Ram distributes (transfers) the rubber through the runner and gate system into the cavities
- Mold remains closed under pressure and temperature to reach optimal cure
- Parts are removed from the mold and the process is ready to begin again

